Colors are widely used in CSS, whether for text color, background color, gradients, shadows, borders… There are several ways to define colors in CSS, each with their own pros and cons.
The color property defines the color of the text. It is pretty straightforward. What is more important is the different types of color units available.
Color names
CSS provides 145 colors names, from the most basic (black, white, orange, yellow, blue…) to the more specific (lawngreen, orchid, crimson…).
body{ color: black;}
a{ color: orange;}Because the color names are hard to remember, and because you probably want very specific colors, color names are not often used.
rgb
Computer monitors, TVs, mobile phones, all use the RGB color model to display colors. Basically, each color is defined by a combination of Red, Green, and Blue. There are 256 possible values for Red, Green or Blue. Because computers start counting at 0 (zero), the maximum value is 255.
Considering a color is the result of a combination of Red, Green and Blue, and because each of these 3 colors have 256 possible values, there are 256 * 256 * 256 = 16,777,216 possible colors available.
Because the RGB model is directly related to how colors are physically rendered, it has become a CSS color unit.
For example, the red color of this website is 219 amounts of Red, 78 of Green, and 68 of Blue:
a{ color: rgb(219, 78, 68);}The black color is no amount of either Red, Green or Blue:
body{ color: rgb(0, 0, 0);}On the other side of the spectrum, white is the full amount of each Red, Green and Blue:
body{ color: rgb(255, 255, 255);}rgba
The rgba color unit is rgb to which we add an alpha value (ranging from 0 to 1, in decimal values), which defines how transparent the color is:
body{ color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.8);}A slightly transparent black color.
The purpose of a color being transparent is to blend with the background, and consequently look slightly different depending on the context. It is particularly useful for background colors.
hsl and hsla
HSL is another way to define a color. Think of it as a color wheel.
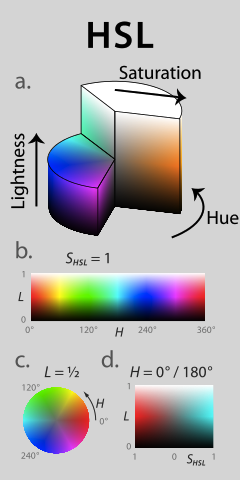
Instead of a color being a combination of Red, Green and Blue, you define:
- the Hue a value ranging from 0 to 360, defines which color you want.
- the Saturation percentage, ranging from 0% to 100%, defines how much of that color you want.
- the Lightness percentage, ranging from 0% to 100%, defines how bright you want that color to be.
Again, the red color of this website is defined this way in HSL:
a{ color: hsl(4, 68%, 56%);}4 indicates it’s red
68% indicates the red is quite prominent
56% indicates it’s halfway between black and white
The hsl color unit is easier to understand than rgb because the expected result is clearer. You basically define a color in 3 separate steps, and can play around with each value to come up with the color you want. If you want a yellow shade, you can start with a value like hsl(50, 68%, 56%), and alter the Saturation and Lightness value to find the specific shade you’re looking for.
I consider hsl to be human-readable, whereas rgb is more computer-readable.
hsla is the same as hsl, with the added value of being able to define an alpha value:
body{ color: hsla(4, 68%, 56%, 0.5);}A transparent red color.
Hexadecimal
Colors in CSS can also be defined with hexadecimal values, like #db4e44.
To understand what hexadecimal values are, let’s look at how binary and decimal work:
| binary 2 possible values | 0 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| decimal 10 possible values | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||||||
| hexadecimal 16 possible values | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F |
Consider the 0-9 numbers and the A-F letters as symbols.
Humans use the decimal system. We have 10 symbols to form numbers.
In hexadecimal, we have 16 symbols to form numbers. Because 0-9 are not enough symbols, we also use A-F. And it starts at zero. So:
- the number
4in hexadecimal is4 - the number
12in hexadecimal isC - the number
16in hexadecimal is10because after you’ve run out of symbols (the last one beingF), you add a second symbol to the left and increment (0becomes1) and the right one starts over (fromFto0)
Do I have to remember this?
Not at all! It is here to provide an explanation of how hexadecimal values work. The most important thing to remember is that there are 16 hexadecimal symbols.
Just like RGB, a hexadecimal color value is a combination of Red, Green, and Blue, each of them being represent as a hexadecimal value, like DB for Red, 4E for Green, and 44 for Blue.
Because Red, Green or Blue can only have 2 symbols, their possible values are 16 * 16 = 256, which mirrors the RGB color unit!
Why not use RGB then?
Usually, when choosing colors, you don’t write them directly. You either use a color picker, or copy/paste it from Photoshop, or choose a colour palette somewhere.
Hexadecimal values are easier to copy and paste, as they only comprise 6 characters.
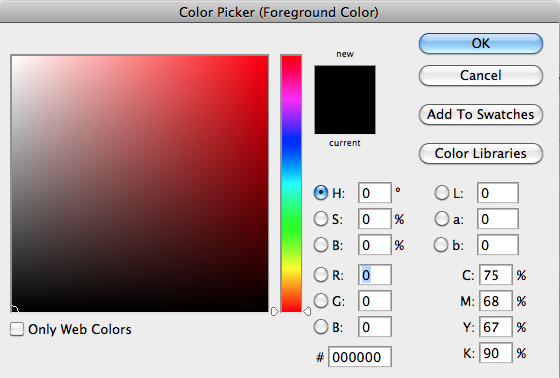
It is easier to copy paste a single field than 3 separate ones.
In CSS, you only need to prepend a hexadecimal color value with a hash #.
Which one to pick?
If you don’t intend to use any transparent color, stick to hexadecimal values, as they are easier to copy/paste and don’t take much space in your code.
If you want some transparency, convert your color from hex to rgba, and use the rgba color unit.
If you want to play around with your color directly in the browser, try hsl.
